The Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architecture has exploded in popularity over the past few years and there’s no sign of it slowing down any time soon.
As security teams seek to push policy enforcement closer to the edge to prevent threats and provide a better user experience, SASE continues to shine as the premier option for simplifying how they implement and maintain their security strategies.
In this Guide
Explore the cybersecurity impact and organizational benefits of the Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architecture with our in-depth guide.
- Introduction to SASE
- How the SASE Architecture Works
- The Five Key Components of SASE
- Securing Access Everywhere and Anywhere with SASE
- Better Data Security with Data-first SASE
- Migration and Implementation Best Practices
- Compliance and Data-first SASE
- Accelerate Transformation with Data-first SASE
- Resources and References
Introduction to SASE
SASE combines networking and security solutions and functionality into a single cloud-delivered service model. Unifying these capabilities reduces costs, enhances application performance and provides better protection for organizations.
Gartner® first penned the concept of SASE in 2019, and circumstances relating to the pandemic accelerated adoption as IT teams sought to support increasingly distributed workforces and IT networks.
In a few short years, SASE advanced from an academic concept to the most common architecture supported by cybersecurity industry leaders. By 2025, Gartner expects a 50 percent increase in the number of vendors with generally available single-vendor SASE offerings, compared to mid-2023.
Bringing networking and security together allows SASE to accelerate performance for end users by enabling direct-to-cloud connections instead of backhauling traffic through a central data center for inspection. Similarly, the unified security services promote a simpler user experience for employees interacting with the applications they need to do their job.
Organizations are introducing new solutions and moving away from dated technologies with SASE, like Virtual Private Network (VPN) access. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a critical part of SASE and allows organizations to avoid the latency that VPNs introduce while still authenticating users and devices for internal application access.
With so many people working from home and coming together from around the globe, SASE solutions are essential for maintaining productivity and ensuring robust cloud security for organizations. SASE empowers remote work, enhances scalability and makes “Bring Your Own Device” (BYOD) policies more secure.
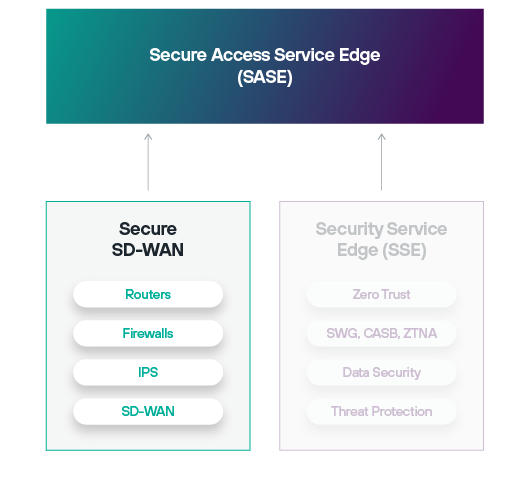
How the SASE Architecture Works
The security and networking sides of SASE are known as Security Service Edge (SSE) and Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN), respectively.
When provided together by a single vendor, these compose the most effective SASE model defined by Gartner® and commonly in use today:
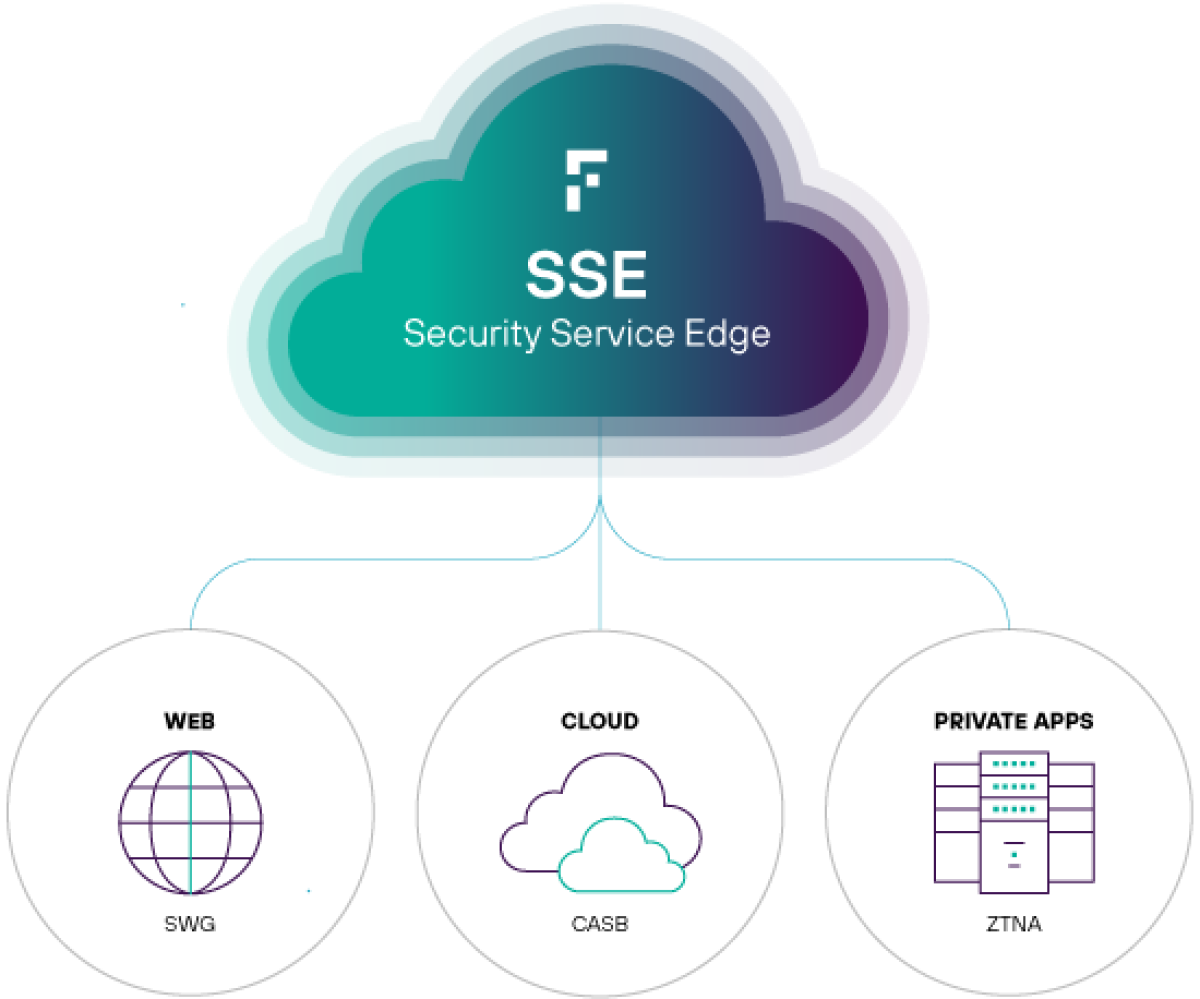
Security Service Edge
SSE secures three key points of access – the web, the cloud, and private applications. It excels at keeping attackers out and sensitive data in.
Unifying this security functionality allows organizations to consolidate access control, data security, threat protection and monitoring under one platform. The individual components of SSE can be incorporated as needed into a security strategy, with the goal of eventually integrating them all together.
SASE optimizes connectivity and reduces latency so that SSE can perform efficiently and with a high-quality user experience
Software Defined Wide Area Networking
SD-WAN enables organization to route and manage traffic more effectively and easily create and extend network policies wherever users are located.
It can reduce networking costs by using any combination of connection types – including MPLS, LTE and broadband internet services – to give users the fastest access to applications and corporate resources. SD-WAN technology can also improve performance by routing traffic more efficiently to optimize bandwidth consumption.
Secure SD-WAN solutions include some built-in security features such as IPS and Advanced Malware Detection, which combine well with a security-focused SASE platform to ensure a seamless and safe user experience
Under a traditional security model, organizations use various point products to protect hybrid workforces from threats. But the disparate security model leads to gaps in coverage, false-positive alerts and poor performance for users. This allows threats to slip by undetected and pushes employees to skirt around the rules, inviting more risk into the organization.
SASE changes all of that. At a security level, it consolidates policy configuration and enforcement within one console, making it easier to manage and maintain. The cloud-delivered security services and improved networking deliver better performance and security for cloud applications, and the agentless coverage adds to a smoother user experience.
The Five Key Components of SASE
There are five essential components you must adopt to successfully implement SASE. These include:

Secure Web Gateway (SWG)
SWG provides protection from malicious websites and enforces company web browsing policies using content inspection filters to protect user-initiated traffic. It may either use a cloud proxy or run directly on the endpoint. Forcepoint ONE SWG forms part of Zero Trust Web Access (ZTWA), which enhances SASE security with two key products and functionalities:
Remote Browser Isolation (RBI): RBI renders risky sites in a remote virtual container, preventing malicious code from infecting the endpoint
Zero Trust Content Disarm & Reconstruction (CDR): Zero Trust CDR extracts valid business information from files, verifies that it is safe, and then builds new files to convey it, preventing even advanced zero-day attacks and exploits
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
CASB secures access to cloud applications and enforces data security policies within them. Forcepoint ONE CASB offers agent-based and agentless coverage to extend protection to any device. It also automatically discovers cloud application use (sanctioned or unsanctioned), analyzes the risks and enforces appropriate controls for over 800,000 SaaS and production applications.


Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
ZTNA provides controlled access to private web apps from anywhere, enabling advanced control over data in use across managed or unmanaged devices. Forcepoint ONE ZTNA delivers access based on the specific context of the user, employing the principle of least privilege and generally offering functions such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On (SSO).
Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) / Cloud Firewall
While SWG, CASB and ZTNA come together to form SSE, firewall technology represents the intersection of security and networking. Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) technology is available through both physical and virtual appliances, but admins who are looking to scale remote work within a SASE architecture will likely rely primarily on cloud-based solutions commonly known as Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS). These can be deployed from anywhere in the world via the cloud, providing visibility and control through centralized management and automation.


Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN)
In addition to eliminating hardware installation and flexibly using whatever connections are available, a secure SD-WAN features built-in security functionality such as multi-layer inspection, intrusion prevention and DNS sinkholing. Forcepoint Secure SD-WAN also ensures that mission-critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and can apply features such as traffic steering and application health monitoring to reduce latency and jitter.
Securing Access Everywhere and Anywhere with SASE
SASE is not the only security framework to have made strides in recent years. Also worth noting is the Zero Trust framework, which calls for all users and devices to be constantly authenticated and validated before receiving access to IT resources within a network. This approach is the opposite of traditional network security practices, where anyone or anything inside the secure network perimeter was considered trustworthy.
But it’s not a matter of choosing between a SASE or a Zero Trust architecture – in fact, any SASE platform worth considering will incorporate Zero Trust principles. The fusion of these two concepts provides the foundation for future-proof data security practices.
This integrated approach to data security is the basis for the Data-first SASE concept pioneered by Forcepoint.
Data-first SASE goes beyond simply securing access. By continuously safeguarding the usage of business data, simplifying security to maximize productivity and reduce operating costs. Key benefits of Data-first SASE include:
Data Security Everywhere – Seamlessly extend data security policies across web, cloud, email, network and endpoint with just a few clicks
Distributed enforcement – Enforce policies across the cloud, edge and endpoint with greater performance
Reliable scalability – Grow with the elasticity of an AWS hyperscaler platform
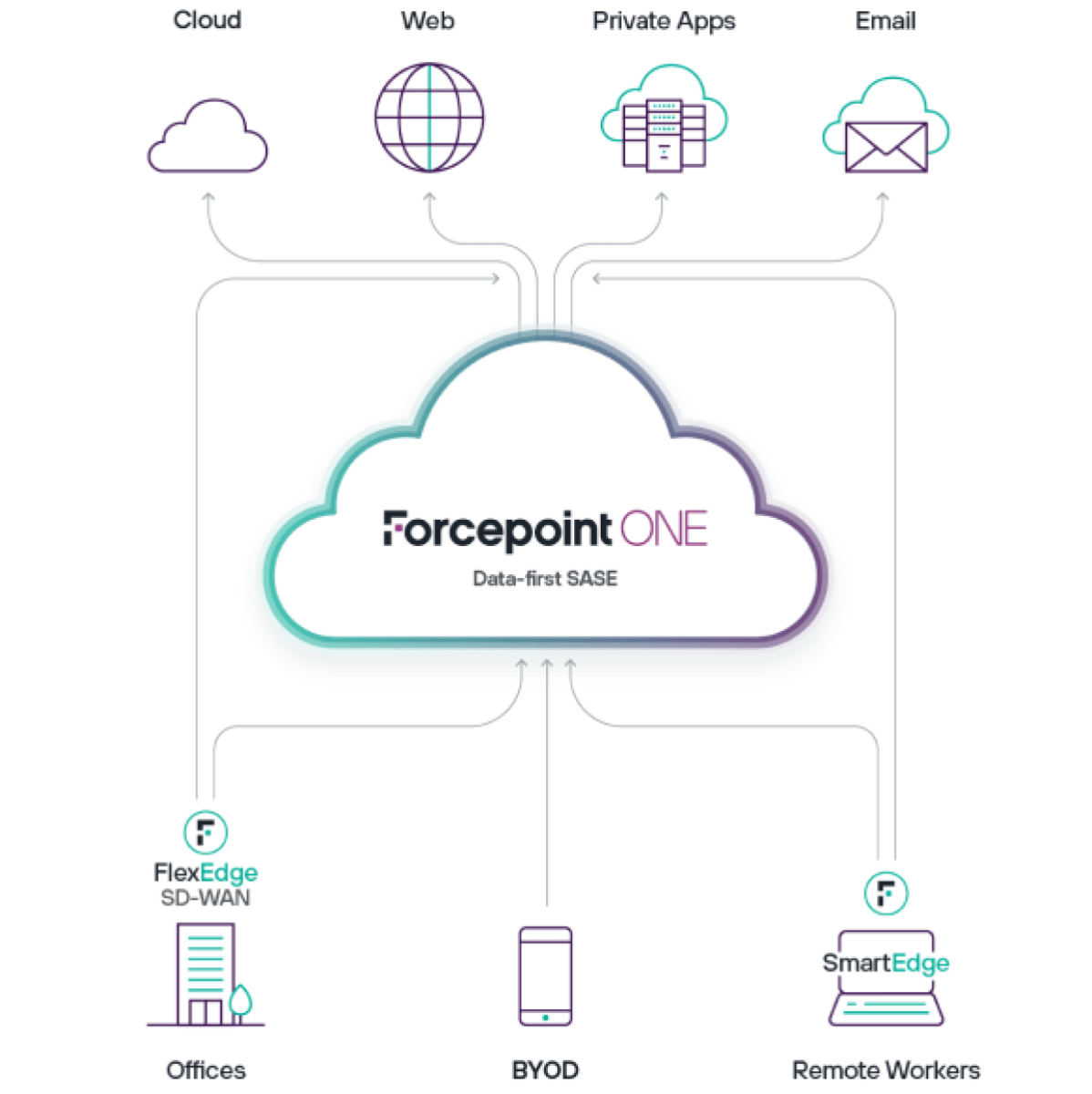
Better Data Security with Data-first SASE
Data-first SASE starts with Forcepoint ONE. The all-in-one, cloud-native security platform pairs performance with security, all within one console.
Forcepoint ONE provides a modular structure that allows organizations to add services as needed and minimize time spent on configuration and training. Security teams can use this to build a Data-first SASE architecture one step at a time, adding to SSE and SD-WAN the additional element of Zero Trust Data Security.
Forcepoint ONE delivers Data Security Everywhere through an integration between Forcepoint ONE and Forcepoint DLP. It allows policy configuration to be replicated across cloud, web, email, network and endpoint with just a few clicks. It capitalizes on the unification that SASE introduces to provide more secure access to data, wherever users are located.
Discover just how easily you can secure your data everywhere.
Key Capabilities and Use Cases for Data-first SASE
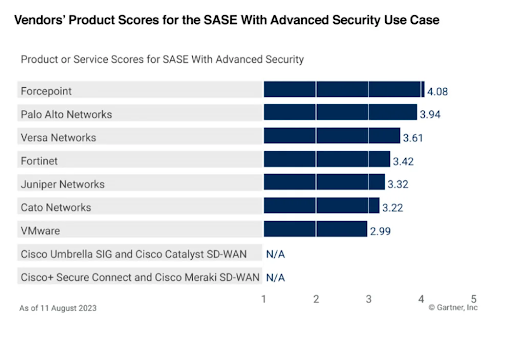
In the 2023 Gartner® Critical Capabilities for Single-Vendor SASE, Gartner identified three key use cases: Basic SASE, Network-Driven SASE and SASE with Advanced Security.
Gartner observed that, “across all offerings, most vendors provide strong branch networking and branch security capabilities. However, the level of advanced security features across all offerings is only mediocre for most enterprises."*
In this report, Forcepoint was ranked as the highest vendor for the Advanced Security Use Case.
Which organizations should be looking for SASE with Advanced Security? Gartner is clear: “This is typically a highly regulated enterprise or one that deals with sensitive information, such as financial services, insurance and healthcare. It is an organization that requires advanced security capabilities, not simply “good-enough” security.”
Benefits and Advantages of Data-first SASE
Prevent known and unknown web-based attacks with SWG, RBI, and Zero Trust CDR.
Apply strong data controls in any cloud app with CASB.
Provide Zero Trust access to private web apps without a VPN with ZTNA.
Connect and protect offices, branches and remote sites with Secure SD-WAN.
Consistently enforce data security policies anywhere data is accessed with Data Loss Prevention (DLP).
Track economic value and security analytics in real-time with Forcepoint ONE Insights.
Migration and Implementation Best Practices
Moving a company to a new security model can be a daunting prospect, but you can find tips and best practices for putting these new systems in place. Below are two guides that Forcepoint has put together to make the process smoother.

The ease of implementing a Data-first SASE security model increases dramatically when the individual products come from the same vendor and are designed to work together. Forcepoint ONE A Unique, Data-first SASE Platform explains the benefits of single-vendor SASE, how Forcepoint differs from other SASE vendors, and how Forcepoint ONE makes Data-first SASE easy to adopt.
Compliance and Data-first SASE
Data-first SASE excels at helping companies achieve compliance with data regulations worldwide. Forcepoint DLP provides over 1,700 pre-defined classifiers and policy templates, which adhere to the data privacy requirements of over 80 countries. Through Forcepoint ONE, these policies can be extended to the different corners of the organization and provide broad coverage and visibility for audits.
It is incumbent on organizations to understand the pertinent regulations and take steps to demonstrate compliance with them. A few of the key regulations that may touch on your business are:
Data Privacy Compliance – Simplified
By consolidating security functions into one single-vendor SASE platform, organizations can more easily apply policies across multiple channels. This makes it easier to flexibly deal with changing or newly applicable regulatory requirements.
Data Security Everywhere is the capability Forcepoint offers to set a policy across SWG, CASB and ZTNA, as well as endpoint and email, speeding changes and saving labor.
Accelerate Transformation with Data-first SASE
Organizations worldwide are focused on digital transformation, seeking out new opportunities to boost business productivity and cut operating costs. Increasingly distributed organizations are re-architecting their networks and security to move their most valuable data and applications to the cloud, in order to provides users with faster, more affordable access to company resources.
Many organizations achieve the reliable, secure connectivity required of the cloud through SASE. SASE provides plenty of organization-wide benefits, including:
Increase to productivity by accelerating the adoption of work-enhancing SaaS/cloud apps
Reduce risk by adding security to direct-to-cloud SD-WAN deployment to keep intruders out
Cut costs by avoiding the need for expensive MPLS connections
Streamline operations by integrating connectivity and security across thousands of sites